Non-fungible tokens (or NFTs) have become a popular feature of the Web3 platform community, with several high-profile public figures launching their own NFT issues. These tokens also lend themselves to numerous uses involving P2P trading and digital payments, which has drawn an unprecedented amount of interest and attention among the public. These tokens and the fundamental knowhow are continually advancing, introducing the next step in the NFTs evolution – dynamic NFTs. So, here we will take a closer look to understand the concept of dynamic NFTs, the mechanism in which the dynamic NFTs work, and also the way in which they can be used.
If dynamic NFTs are of interest to you, this article will be expanding on this concept during our exploration. We’ll start out by looking at what a dynamic NFT really is. Following this, we’ll take a closer look at how the mechanism behind a dynamic NFT functions. Finally, we’ll compare dynamic NFTs to the idea of static NFTs. Furthermore, we will study and find some strong cases where the application of dynamic NFTs can be seen and also better understood and we can get an insight on why they are helpful.
Understanding NFTs
Before we deep dive further in understanding the concept of dynamic NFTs, let’s go back and analyze the NFTs. Having a brief understanding of the non-fungible tokens can serve as a good starting point for enthusiasts to have a better understanding of dynamic NFTs.
NFTs are a simplified abbreviation for Non-Fungible Tokens, also known as tokens, and constitute an entirely distinctive class of digital assets that persist on the blockchain. Each NFT is unique and has a contract address and token ID that is guaranteed to be different from others. You can attach images, files, data, links, etc., to the NFT’s metadata.
NFTs for art world
The majority of NFTs are currently deployed for digital art; an artist may mint a token representing a digital art piece, and a collector can purchase that token, indicating ownership. Once NFTs are minted, their token IDs don’t ever change. Remember that ascribing metadata, which includes an NFT’s description, an icon, and more, is optional. In its most simplified form, an NFT is simply a piece of art. Furthermore, once an NFT is created, the supply permanently contains the token ID and metadata, which are static, while these tokens also behave in a manner that facilitates communication.
Static NFTs features
The advantages of this static NFT model, which is devised for online artists, include the ability to quickly clamp down or even keep track of unauthorized distribution of their original artwork. Previously, artists did not have the right tools to tell the difference among files and to distinguish different files from one another, and hence they could not monitor or shut down the distribution of their art, especially among third parties. In this age of NFTs, artists can sell artwork digitally to their fans by giving them exact ownership, and fans can sustain ownership when an original artwork is stolen or distributed through the web, proving that they own the artwork.
Cryptocurrency enthusiasts were quick to follow NFTs, which have led to billions of dollars in investment. The blockchain art market has experienced tremendous growth in a short time, with investors pouring billions of dollars into it every year. Its long-term growth is projected to continue at more than 10% a year until 2030, promising wealth for artists and collectors.
Despite the attractiveness of the NFT market, there are two major downsides. First, folks occasionally repost other NFTs inappropriately. The second is a difficult challenge related to the movement of NFTs across the blockchains. Both of these pain points can be fixed with the disruptive revolutionary dynamic NFT. We further explore its impact on NFT enthusiasts.
The Static NFT collections such as the famous bored ape yacht club, Cryptopunks, and The Sandbox traded a constant amount of ETH, providing evidence of immense consumer excitement around it and also user faith in the prospect of NFTs. But now, times are changing too fast. Now, the NFT world has something different to offer. It’s the dynamic NFTs that is believed to be going to redesign the NFT market scene forever.
Dynamic NFTs are coming on strong in the crypto market, and some such as merge and OG crystals have made waves in the crypto market. Many industry experts believe that dynamic NFTs will be the next big thing in the next few years, so it’s important to familiarize yourself with the future – dynamic NFT creation process, what sets the dynamic NFTs apart from the static and create your own piece of this market.
Dynamic NFTs are a new type of digital asset that can be used in video games. They represent unique avatars, and as players progress through the game they need to update aspects of their token’s metadata with external conditions so it reflects effort put into playing – this essentially means dynamic non-fungible tokens retain an identifier while allowing updating certain properties based on demand from other variables.
How Does a Dynamic NFT Work?
Dynamic NFT accords (non-fungible tokens) can evolve depending upon off-chain and on-chain functions, and the technology responsible for this operation is smart contracts. When a NFT (non-fungible token) is initiated, smart contracts make a decision based on the computations of the off-chain and on-chain data to decide on the response that’s exhibited to the users.
It is only on the computations of both the off-chain and on-chain data that the smart contract provides responses – one or two to the requestor.
Basically, it implies that smart contracts are largely responsible for allowing the NFTs to alter, update, and also expand over a certain duration. Hence, whether the NFTs should change or not is determined by the smart contracts and if it has to alter it then it does so with modifying the metadata of a dynamic NFT basis the on-chain and also the off-chain data.
With an in-depth understanding of the way that the dynamic NFTs work and also what exactly it is, we can also garner some knowledge on how to create it. Having a clear understanding of the important components of smart contracts, intricacies of the smart contract development and explanation of web 3.0 is also essential.
Comparison of Static and Dynamic NFTs
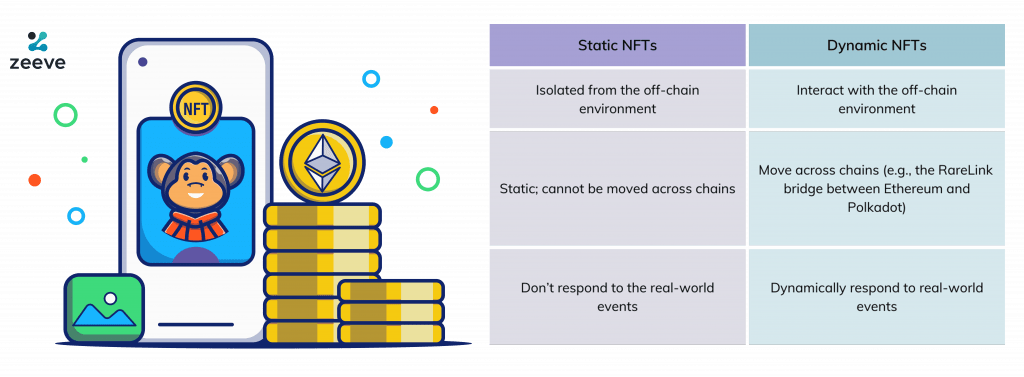
Users are far more likely to be familiar with static NFTs today. A static NFT is a non-fungible token with decrees that cannot be altered. These tokens contain pictures, videos, music, objects in a game, and much more. In some instances, such as in digital art or digital collectible items, static NFTs can be an especially attractive choice. After all, it’s their written permanence that makes them so useful and unique.
Although still far from widespread use, the next phase in the progress of NFTs (non-fungible tokens) is dynamic NFTs, and these could be quite useful in the coming months and years. The future of ownership is here. The dynamic NFT token allows you to own part or all the data in a storage system, which can be verified through blockchain technology. These tokens combine some unique qualities from static NFCs with input derived using both centralized AND decentralized databases; they also allow exchange on either chain for increased convenience!
Dynamic NFTs can use data from both on-chain and off-chain resources to allow the metadata of the tokens to differ. Consequently, the ability to modify a token’s metadata distinguishes static from dynamic NFTs.
Hence, both static and dynamic NFTs can handle unique use cases, and only one is unlikely to overshadow the other, which indicates the potential for both static and dynamic NFTs to become popular within the crypto world. The development of dynamic NFTs in the blockchain space, however, provides more versatility and builds awareness of the tokens and increases their versatility.
We need to learn more about some scenarios for which dynamic NFTs will come in handy so the distinction between these two types of NFTs becomes even more apparent.
Relevance of Dynamic NFTs
With the evolution of the NFT world, dynamic NFTs have also come to symbolize the next step in the wave of advanced technology solutions. The VRF component of dynamic NFTs ensures the authenticity and equality of item distribution during game events. That’s why P2E designers can enjoy fair and impartially apportioned rare properties and power rankings during gameplay events.
Dynamic NFTs are advantageous due to the fact that they can change dynamically based on a real-world event transmittal to the blockchain via oracles. As an example, if you happen to possess an NFT gift card that has an image of a baseball athlete and once he becomes a champion, the card may also show the title of your idol, altering its code based on the real-world output.
Updated dynamic NFTs enhance authenticity, making them applicable for various purposes. As an example, you can have an NFT to serve as a passport, helping you to travel across different countries with no elaborate documentation and stamping required. All modifications are reflected in the NFT’s code, so it is impossible to defraud or scam it. The exact same applies to banking accounts, educational certificates, insurance, and many other documents.
Dynamic NFT Use Cases
In the previous section, we stated that in-game avatars are a potential use case for individual NFTs, but this is just a mild instance of the versatility and flexibility of dynamic NFTs in general. Therefore, we made the decision to include two additional use cases in this chapter designed to illustrate their many benefits. This will help you better answer why these NFTs dynamic are? The additional scenarios may illustrate things more clearly.
· NFT Sports Cards
· Real Estate
NFT Sports cards
The first thing we take as an example is sports cards, and in this case, we’ll give a football illustration. We’ll say that we have a dynamic NFT representing an actual football player. The NFT could have various information such as speed, body weight, height, goals scored, assists, agility etc. stored in the token’s metadata.
As time goes by, the data generated by a player throughout the season will likely vary, as, for example; he will score a few goals. The dynamic NFT can automatically update metadata based on that info, unlike the static NFT. However, there is no possibility of this happening with a static NFT; since metadata would be permanent following someone creates the initial token.
Real Estate
In the second instance, we’re utilizing a house to safeguard our arguments. Take for example the case of a dynamic NFT demonstrating a house. When tokenizing the assets of the real world, it’s useful to be able to change metrics, which is quite frequently the case.
In this example, we hope to alter the metadata of a NFT (non-fungible token), which relates the changes that might occur to the property, may be of interest to future investors. So, for example, the metadata should contain valuable information with regard to the history of the property, its maintenance, time since it has been founded, market worth, past deals, and so on, so assets such as property can be tokenized. Tokenizing real-world assets as data incentivizes the development of methods to mass-update the metadata of valuable assets such as land.
Advantages of Static NFTs
When the NFTs market took off, the market cap grew beyond $18 billion. Static NFTs, a type of smart contract, hold attributes of being absolutely immutable and permanently recorded on the blockchain. We should remember, however, that inalterability is the standard of blockchain, thus rendering it an excellent medium for verification of immutable transactions and data for scam prevention.
Advantages of Dynamic NFTs
Dynamic NFTs have a fluid smart contract, which allows the NFT to vary over the passage of time according to real-world conditions. This can be used for multiple reasons, from loading an NFT to a different blockchain or changing the user’s outlook upon the change of ownership. Dynamic NFTs also have various use cases; some are used for blockchain-based ticketing, some for P2P transaction subscriptions, and others for P2P transfer ownership of physical objects.
Dynamic NFTs can also serve a variety of other purposes, including ticketing to game show unit purchase and game trade name usage. In addition, they are expected to possess the verifiable randomness function (VRF), like with the dynamic Shield NFT on Solsea.
Final thoughts
The emergence of NFTs was facilitated by blockchain’s increasing importance. However, NFTs that most people are familiar with are static NFTs; meanwhile, the newest advancement in the Web3 community is dynamic NFTs.
The way dynamic NFTs behave is in some respects similar to static ones, but the term dynamic in our example refers to the token’s ability to update its metadata parameters based on both off-chain and on-chain data. This is different from the static NFTs that one can mint.
Dynamic NFTs are attractive because of their capability to easily update their metadata. A good example is a real estate property, where a dynamic NFT presents various attributes concerning the property. In the instance where there was such a modification, the dynamic NFT would have the capacity to supplement its attributes with, for example, a maintenance history and past sales.
Real estate is merely one of countless essential applications of dynamic NFTs. Given these characteristics, NFTs are believed to significantly expand the variety of NFTs and their components, which can significantly impact the sphere.
Strategise your way into the NFT domain
Zeeve is the primary Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) platform that supports businesses and blockchain start-ups to build, deploy and manage decentralized apps and blockchain networks. It serves as a low code automation platform that supports several blockchain protocols with cutting-edge analytics. It not only deploys and builds the networks but also monitors the nodes. Explore the dominant set of APIs to set up DApps for a series of use cases across several verticals. With an experienced and expert team of blockchain solutions providers, we support applications in all spaces. Get to know more in detail about the blockchain as a service offerings, nodes and smart contracts by calling us!