The word cross-border refers to payments across different countries. Cross-border payments are vital to individuals, businesses, merchants, industries, and international development organizations. However, cross-border transactions are often inconvenient due to their exorbitant fees and lengthy processing times. The use of blockchain in cross-border payments will make the entire process simpler. The global economy will get an uplift by using blockchain technology for cross-border payments.
Distributed ledger technology or blockchain technology is a game-changer move in cross-border money transfer. It accelerates the payment process by employing encryption technology. At present many blockchain-based payment platforms already exist, and many more will come in the future.
In this blog, we will take a look at the existing cross-border payments system and how blockchain technology is swifter and more efficient. We would also evaluate the major changes that industries foresee and what the future beholds for the use of blockchain in cross-border payments.
How do regular cross-border payments work?
Various global messaging systems operate the traditional international transactions, and it connects a network of banks. A remittance transfer does the transaction. A remittance transfer is a monetary transaction along cross-borders by a company that associates with — banks, credit unions, or financial service institutions.
Majorly, a remittance transfer takes less transaction fee than a bank transfer. In traditional cross-border payments, the ledger isn’t the same between the sender and receiver. Thus, adding a security concern to the whole settlement process. One of the examples of a remittance transfer channel is SWIFT.
It redirects transactions by applying a coded messaging system. Businesses and individuals have to sign-up with a payment service provider to receive an international payment. This acts as a gateway for payment.
While the traditional system often fails on traceability. And due to mediator banks in between, the transaction process becomes cumbersome along with a hefty fee. In addition, the trade differences between countries make the process more complex. There are several legal restrictions in certain countries. The fees or the taxes can be in the form of customs duty or value-added tax, which vary from one country to another.
Why opt for a Blockchain Network for Transactions?
First of all, immutability is not compromised in the blockchain. The centralized authority is replaced here by a decentralized network. Here, a network of nodes verifies the monetary transaction. As in the traditional cross-border payments – due to various detours in bank branches, a simple peer-to-peer transaction becomes more perplexing. Here, the transaction gets completed in real-time in the blockchain network due to fewer negotiators. Various public blockchains are global and can transfer money anywhere in the world.
While it takes on an average 3-5 days for the transaction to occur, there are errors in transactions sometimes, and it fails in between. However, blockchain supports transparency and traceability. The network solves the pain points of a lot of different industries. Simply put, all the transactions are done quickly with a low transaction fee.
Global Economy of Cross-Border Payments
The global cross-border payments will reach US $156 trillion in 2022. Thus, confirming it as a trillion-dollar market. According to Juniper research, solely the B2B cross-border payments will be a $35 trillion economy in 2022.
Traditionally, the transaction was done by a correspondent banking network (CBN). However, as the technology grows, we witness cross-border payments with distributed ledger technology. According to the world bank report on remittance prices worldwide, the average cost of remittances is around 7%.
In recent years, G20 countries have been on a mission to lower cross-border remittances to 5%. With the emerging trends, organizations such as G20 want more and more countries to participate in the global economy.
As consumers become aware, they are less willing to pay the transaction fee. With the increase in the digital payment methods for remittances, customers are looking for cheap cross-border payment alternatives. And the blockchain has a low transaction fee and can easily accomplish this. The new trendsetters in cross-border payments are countries from North America, Latin America, Asia, and Africa.
Industries thriving on Cross-Border Payments
Multiple examples demonstrate that using blockchain for cross-border payments is faster and more feasible. Banks do the processing of cross-border payments in the majority of the B2B industries. The transactions can be for any individual, banking institution, or industry. The applications can be official development assistance (ODA) for international remittance.
In the past couple of years, B2B industries have been accelerating towards digitization. They are adding so much economy to the global workforce. Only cross-border payments across the USA and UK account for 26% of the total annual sale.
When it comes to understanding industries that can benefit from blockchain in cross-border payments, the list goes on and on.
Still, a few major industries reaping the benefits of blockchain-enabled cross-border payments are – food and beverages, hospitality, accounting, E-commerce, oil and gas, air travel, stock trading, crowdfunding, and many more.
The point to be noted here is that blockchain will not only improve cross-border payments but will also boost the overall health of any industry by securing supply chain management, logistics, etc.
Features of Blockchain
Cross-border payments employing blockchain as its intermediary technology is a significant advantage. Merging the blockchain technology with cross-border payments is a win-win situation for both the sender and the receiver. A few of the features of blockchain technology are:
Non-tampered information
By using blockchain in cross-border payments, tampering with information is difficult. The blockchain architecture has every block with information linking it with the previous block. The database is distributed, and every participant owns a copy of the transactions.
Real-time Payment
For businesses that need funds quickly, real-time payment is a game-changer. The payment happens instantly with transaction information integrated into it. Liquidity management becomes easier in real-time payments for businesses.
Decentralized
In regular cross-border payments, financial institutions follow data privacy regulations. Various banks have different regulations. The flow of clients’ information across various jurisdictions – can be prevented easily by using blockchain technology for cross-border payments.
No intermediaries
Blockchain establishes direct contact between the sender and the receiver. The receiver has direct access to the payment. There are no delays, unnecessary fees, or remittances involved.
There is efficiency with many advantages, and the security is beefed up. The blockchain network solves the credit barriers exceptionally. Overall, it provides a framework for cross-border transactions.
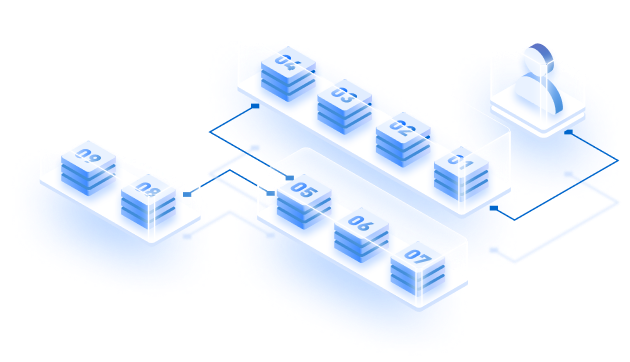
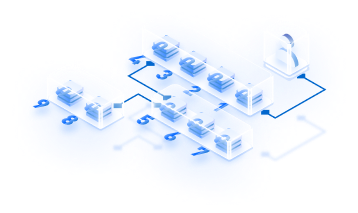
How blockchain works for payments
Here, the two crucial parts of the transaction are the gateway and the customer; no banking institution in between. A person living in the US can send money to Italy using an on-ramp service provider.
The provider will convert the Fiat money into cryptocurrency. The cryptocurrency can be kept in a crypto wallet. One can find multiple crypto wallets, choose anyone, and set up an account; after that, one can initiate the transfer from a bank or credit card.
Finally, you need to have the address of the receiver’s wallet to send the required amount to the receiver. Once the money reaches the receiver’s wallet, the receiver can convert it into fiat money after receiving the cryptocurrency. Crucial steps to transfer money are:
- A consumer or a business wants to purchase a product or a service. Here we require consumer ID, retailer ID, amount of transaction, and timestamp.
- Smart Contracts are for implementing currency exchange according to the real-time exchange rate.
- On the block recording of all the information regarding the transaction is done.
- The information in the block is added to the blockchain consensus mechanism by following a technical regulation.
- The value of the previous block’s hash is added to the new block. This is an essential step to making the chain tamper-resistant.
- The same information is updated on the node as well. The node broadcasts the information further. The block gets verified.
- Finally, the transaction is completed, and the cryptocurrency reaches its destination.
Significant changes due to Blockchain-enabled Cross-Border Payments
Even the major mainstream financial companies have started to use the blockchain to pilot transactions. The upper layer technology remains the same, and a little tweak in the core makes it work on blockchain.
In the future, the whole scenario will divide into two types where either the mainstream financial institutions will use blockchain networks in a centralized form. Or blockchain companies completely changing the existing currencies with cryptocurrency.
If the latter happens, stablecoins will also play a role in the transaction process. More and more stablecoins will become popular. As volatility is always in crypto, many users are hesitant to use it. Thus, stablecoins will be helpful to balance the volatility.
Also, government organizations are steadily deploying blockchain technology to manage financial settlements, enhance existing legal frameworks, and grant disbursements.
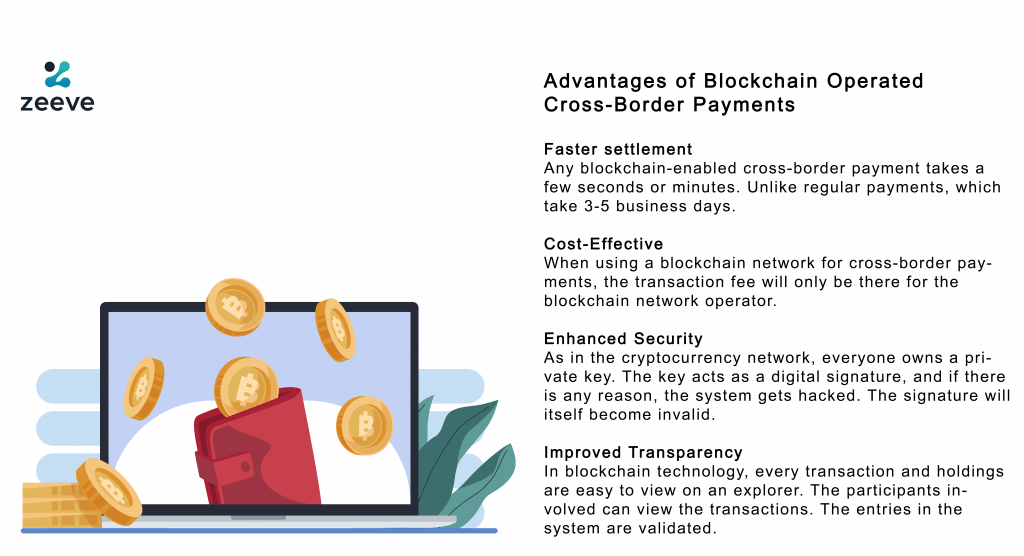
Advantages of Blockchain Operated Cross-Border Payments
Cross-border payments employing blockchain as its intermediary technology is a significant advantage. With the onset of online business, there has been a surge in cross-border payments. A few of the advantages related to using blockchain in cross-border payments are:
Faster settlement
Any blockchain-enabled cross-border payment takes a few seconds or minutes. Unlike regular payments, which take 3-5 business days. Various issues such as time-zone differences and currency value differences do not affect the transaction time as the cryptocurrency is a globalized currency. The average time is somewhere in the range of 141 minutes to six minutes. When all the transactions happen online, it eliminates the burdensome office activities.
Cost-Effective
Banks have to take the help of intermediary banks to process the transaction. As often, banks don’t have an alliance with the bank in the other nation.
The third party in between charges a fee, and the cost is divided between the sender and the beneficiary. When using a blockchain network for cross-border payments, the transaction fee will only be there for the blockchain network operator.
Enhanced Security
As in the cryptocurrency network, everyone owns a private key. The key acts as a digital signature, and if there is any reason, the system gets hacked. The signature will itself become invalid. As we know, the blockchain is synced simultaneously. Thus, an attacker would not be able to access the information across multiple computers quickly.
Improved Transparency
In the future, traditional financial reporting companies will become obsolete. As in blockchain technology, every transaction and holdings are easy to view on an explorer. Even for a private permissionless blockchain, the participants involved can view the transactions. The entries in the system are validated. By sharing the information across the platforms, there will be a reduction in data discrepancy.

Challenges and Closing Thoughts on Blockchain for Cross-Border Payments
The major challenge is that the majority of the citizens are still not well-equipped with the technology. There isn’t much clarity regarding the regulation of the cryptomarket. The Fintech giants such as Wise or SWIFT are currently hesitant to use distributed ledger technology. These payment platforms will deploy blockchain networks when more and more central banks adopt the distributed ledger technology for cross-border payments.
Honestly, banks are not ready to accept the volatility of crypto. It is one of the major reasons for financial institutions not deploying the blockchain for negotiations. Therefore SWIFT has started the new GPI system for settling the transaction. Recently, SWIFT has also collaborated with RIPPLE to streamline the payments from the blockchain.
Blockchain in cross-border payments is increasing day by day due to many shortcomings in the traditional methods. Blockchain technology will leave a profound impact on cross-border payments structure. It can be a technological breakthrough as there is a gradual weakening of the existing payment models. Although, research and experimentation are a part of emerging trends. We are sure that this will leave an overall positive impact on cross-border payments.
About Zeeve
Zeeve is the leading blockchain infrastructure platform for deploying, monitoring and tracking nodes. We help enterprises and Blockchain startups to build, deploy and manage reliable web3 infrastructure. Zeeve is a low code web3 DevOps automation platform. Our platform is cloud-agnostic and supports multiple Blockchain protocols with advanced analytics and monitoring of nodes and networks.
We feature a robust set of APIs to build DApps for a plethora of use cases across industries, including asset tokenization, NFTs, DEX, Stablecoins, etc. Zeeve supports Decentralized Finance (DeFi) space with decentralized storage, trusted nodes, and smart contracts.To learn more about Zeeve, join us on Twitter and Telegram.