Optimism’s superchain was launched just a year ago, but it has achieved immense popularity as a standardized, easy-to-deploy framework for facilitating rapid development of next-gen OP Stack chains. The OP stack framework basically breaks down the complex process of building optimistic Rollups chains into a simplified process by offering a complete set of software components, tools, and frameworks.
With time, Op Stack evolved to become a full-fledged stack. Speaking about the most highlighted addition to OP Stack Rollups after Bedrock upgrade is Superchain. Since the launch of superchain, OP mainnet and all the other OP Stack chains have merged to form a unified ecosystem of superchain. In this Optimistic Rollup guide, we will dive deeper into the concept of Opstack and Superchains. We understand OP stack and Superchain’s value proposition in enhancing the capabilities of Layer-2 scaling solutions.
Understanding OP-Stack
OP-Stack is a standardized, open-source, and shared developer stack that enables projects to build standalone OP rollup chains. Op Stack includes different modular components that together form the infrastructure for the Optimism network. OP stack offers ready-to-use modules that web3 projects can leverage based on their project’s requirements to retain utility, simplicity, and extensibility in their chains. Modules on OP Stack are simple and easy-to-use . And, being open-source, anyone can leverage them to build their Rollup chain. However, these modules are extensive so that developers can customize them to serve the use case-specific needs.
The Idea of OP Superchains
Given that OP Stack allows Optimistic Rollup chains to be deployed on a common infrastructure, Optimism brought the idea to enable a high degree of interoperability across different chains. This forms an interconnected ecosystem of Layer-2s– known as OP Superchains, enabling independent Layer-2s to seamlessly interoperate and transact. By offering this shared development stack, the Superchain allows web3 projects to build OP Stack chains that not only provide unprecedented scalability and customizability but also allow the applications to tap into interoperability. Superchains also achieve cross-chain messaging across various OP Chains through Optimism bridge that sits between OP Stack chains and Layer-1 blockchains like Ethereum.
Besides enabling cross-chain interoperability, Superchain also eliminates the security trade-offs that come with the traditional multi-architecture of blockchain. For this, Superchain enables horizontal scaling, which maintains compliance despite the more number of chains added in the network. And, most recently, Optimism announced that superchain now supports Layer3s, which means that projects can deploy their L3s on top of Layer2s like OP Mainnet, Base, or Mode. Due to all these features, Superchain is identified as the next big upgrade after Optimism’s Bedrock.
The architecture and different layers of OP Stack
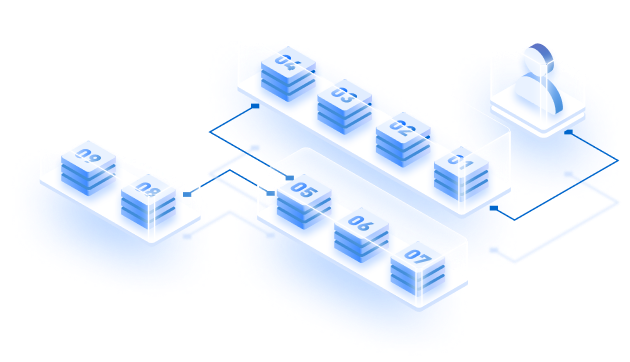
The standard architecture of Rollups built with OP Stack includes different stack layers and specific modules that allow for the building of high-performing Optimistic Rollups. Speaking about how an OP Stack chain performs L2-specific functionality, let’s understand the whole mechanism through the below image which explains the following five core concepts–
- Execution Node: op-geth
- Rollup Node: op-node
- Proving scheme: Cannon
- Batch submission of L2 blocks
- Derivation of L1 Block data
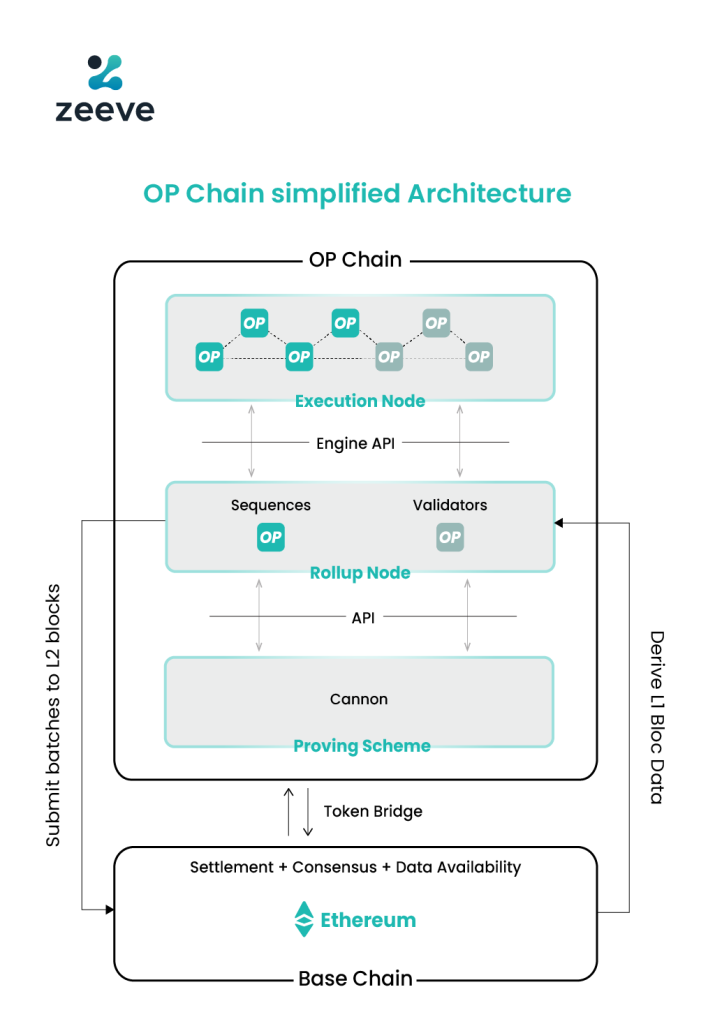
1. Execution node: Op-geth is an extended Ethereum’s execution client that can handle specific functionality on Layer-2 rollups, for example– accepting token deposits from Layer-1. This layer of the OP Stack defines all functions responsible for mutation of the execution state. Here, State transitions are triggered based on the inputs received from the Rollup Node (sequence and validators) via Engine API.
2. Rollup node: OP-node or Rollup node include sequencers and validators. This node can be run both in the sequencer and verifier mode. Here, Sequencers are in charge of batching the processed transactions from Layer-2 and posting them on the main L1 chain. Sequencers define the way transactions on a OP Stack-based chain will be collected and published. Whereas, validators/verifiers check the validity of the batched transactions and submit proof against any fraud if detected.
3. Proving scheme: Cannon is an updated version of Geth that is responsible for running EVM within VMs during the stage of fraud detection and proofing. It’s basically an on-chain dispute engine that coordinates with sequencers and verifiers via API for the purpose of proving a faulty transaction.
4. Batch submission: Sequencers once batch all the processed transactions, and verifiers validate it, then Sequencers submit the batched transactions to Layer-1; Ethereum.
5. Derivation: Derivation allows sequencers and validators to derive raw data from Layer-1 to process them and form final inputs that are provided to the execution layer for passing the transaction load off this chain. To accomplish this task, the Derivation layer can use Standard Ethereum Engine API and the current system state.
All these first three components– execution node, rollup node, and providing scheme interact with base chain (Layer-1) through a token bridge for the purpose of final transaction settlement, achieving consensus, and data availability.
Who all are building Rollups using the OP-Stack codebase?
Optimism’s Superchain ecosystem currently has 40+ chains which contribute a TVL of whopping $15.7B. Coinbase, Gitcoin, and Zora have already launched their OP Stack chains. Coinbase, being the most prominent name, has recently launched an OP stack-based rollup called Base. With this, Coinbase has planned to bring its 100M users on the rollup chain, thereby creating no network congestion on its main chain.
Regarding Zora, they use OP Stack to build their OP Stack-based rollup chain and thus expand their Ethereum-based project for millions of new artists, creators, and worldwide communities. Their Rollup launch will make their transaction on Ethereum cheaper while increasing throughput and enhancing overall user experience.
Also, BSC chose the Optimism Roll-Op Stack to launch opBNB for leveraging their maximum modularity to enhance performance. BNB claims that their OP based chain– opBNB achieves 4000+ TPS, and it can offer 1 second block time with a transaction fee lower than $0.005. Hence, launching the OP stack chain seems a great fit for BNB.
The efficacy of the Op-Stack rollup solutions attracts other players as well as World Coin, Mode Network, Redstone, Mint Blockchain, and Lisk that are contributing to superchain’s growth.
How can Zeeve RaaS help you launch your own rollups?
We’ve covered all the important aspects of Op Stack & superchains in this Optimistic Rollup guide. Now, if your next step is to launch an Optimistic rollup, explore Zeeve’s RaaS stack. Zeeve’s Rollups-as-a-Service supports seamless launch of OP Stack chains with its low-code deployment sandbox and a set of plug-n-play dev tools. The team at Zeeve has deep expertise in the OP Stack framework, its already-built modules, tools, and codebase. Zeeve removes your hassle of managing infrastructure, running nodes, or getting crucial components ready such as explorers wallets, testnet faucets, and data indexers. And, if you envision a modular chain, leverage 40+ third-party rollup service integrations supported on Zeeve RaaS.
On top of this, Zeeve monitors all your Rollup chains on critical parameters while maintaining 99.99% uptime and cutting-edge performance. With Zeeve, you get access to a graphical, real-time dashboard showing the performance of your Rollup chain with details like uptime, disk usage, storage running out, and current block height, etc. Zeeve guarantees the reliability of its Rollups-as-a-service offering with ISO 27001 and SOC 2 Type 2 compliance and enterprise-level SLA.
If you plan to launch a Rollup chain or migrate your dApp to a standalone rollup chain, Zeeve simplifies each of these processes. For more information on how Zeeve is simplifying Rollup launch, connect with our experts or become a part of our active community discussion.