Blockchain technology has undoubtedly revolutionized various industries, promising enhanced security, transparency, and decentralization. In the rapidly evolving landscape of blockchain technology, one of the most pressing challenges faced by developers and businesses alike is the blockchain trilemma, which refers to the trade-off between scalability, security, and decentralization. Balancing these three pillars has been a long-standing issue within the blockchain community. But now, a groundbreaking solution has emerged to tackle this trilemma head-on: Shardeum. By harnessing the power of sharding, Shardeum aims to provide a scalable, secure, and decentralized blockchain ecosystem, offering a promising future for the blockchain industry. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of sharding and delve into how Shardeum is paving the way for a new era of blockchain technology.
Understanding the Blockchain Trilemma
Consider the scenario where you assume the role of a superhero entrusted with the crucial mission of safeguarding the world from an imminent catastrophe. Your decision-making process involves selecting two superpowers out of three available options: flight, super strength, and invisibility. It is important to note that you can only possess two powers simultaneously, adding an element of strategic choice to the equation.
Analogously, the concept of the blockchain trilemma presents a similar predicament within decentralized networks. In this context, the three superpowers are decentralization, security, and scalability. Just like our superhero protagonist, decentralized networks face the constraint of being able to possess only two of these superpowers concurrently.
Importance of blockchain trilemma
The blockchain trilemma holds considerable significance in the realm of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology and was originally introduced by Vitalik Buterin, the co-founder of Ethereum. This term describes the challenge faced by blockchain technology, where it is difficult to achieve all three fundamental properties simultaneously: security, scalability, and decentralization. According to Vitalik, it is typically only possible to have two of these properties at a given time, inevitably sacrificing the third one. As security plays a crucial role in public blockchain platforms, they frequently face the trade-off between scalability and decentralization when making decisions.
Bitcoin, the pioneering and widely recognized blockchain-based cryptocurrency, exemplifies the blockchain trilemma in practice. Bitcoin prides itself on its high degree of decentralization, with numerous nodes dispersed worldwide. This decentralized nature enhances its security, as no single entity or collective holds control over the entire network, bolstering its resilience against potential attacks. Nonetheless, Bitcoin faces challenges when it comes to scalability as it can only handle a restricted volume of transactions per second. Consequently, during periods of heightened demand, the network can experience congestion, leading to elevated transaction fees. In comparison to established credit card processors like Visa and Mastercard, Bitcoin falls short, as these competitors can swiftly process transactions within milliseconds.
Although layer 2 solutions and applications have helped alleviate the scalability problem, the advancements made so far have been mostly incremental in order to meet industry requirements. While the goal is to transition from Web2 to Web3, it is important to recognize that Web2 offers a user experience that is familiar and efficient on a global level. For Web3 to effectively replace Web2, it must significantly increase its throughput capacity to facilitate widespread adoption and enable the full realization of blockchain’s inherent benefits, such as enhanced security, privacy, and decentralization.
Shardeum as a solution to the Blockchain Trilemma
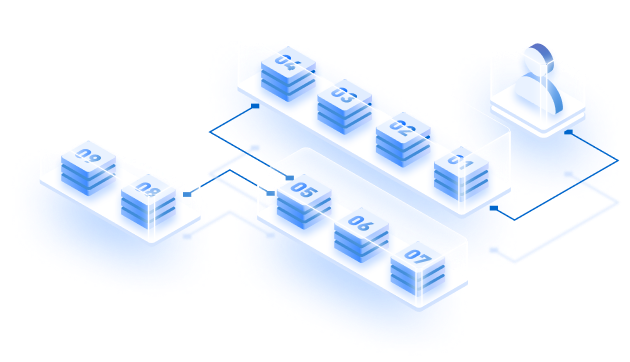
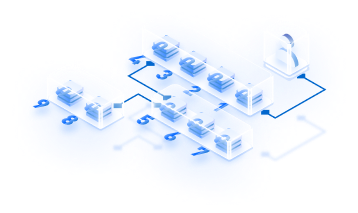
Sharding has been a familiar concept in the blockchain industry for quite some time and has been extensively explored by prominent layer 1 blockchains like Ethereum. It has been long recognized as an effective solution for improving scalability in various applications, particularly within centralized databases. But how does sharding actually enhance the scalability of centralized networks? Put simply, sharding involves dividing the task of validating and confirming transactions into smaller, more manageable fragments, known as shards. While sharding is undoubtedly the most effective approach to addressing scalability concerns, implementing it in blockchain-based networks is considerably more challenging compared to centralized databases.
Shardeum brings forth an encouraging development as it implements a unique approach to consensus and processing, operating at the transaction level instead of the block level. Furthermore, the network employs dynamic state sharding to distribute the computational workload, storage, and bandwidth evenly and dynamically across all nodes. This groundbreaking technique enables parallel processing of transactions and significantly reduces the burden on validator nodes, as they only need to store the state data of the transactions they are directly engaged in.
Dynamic State Sharding in Shardeum
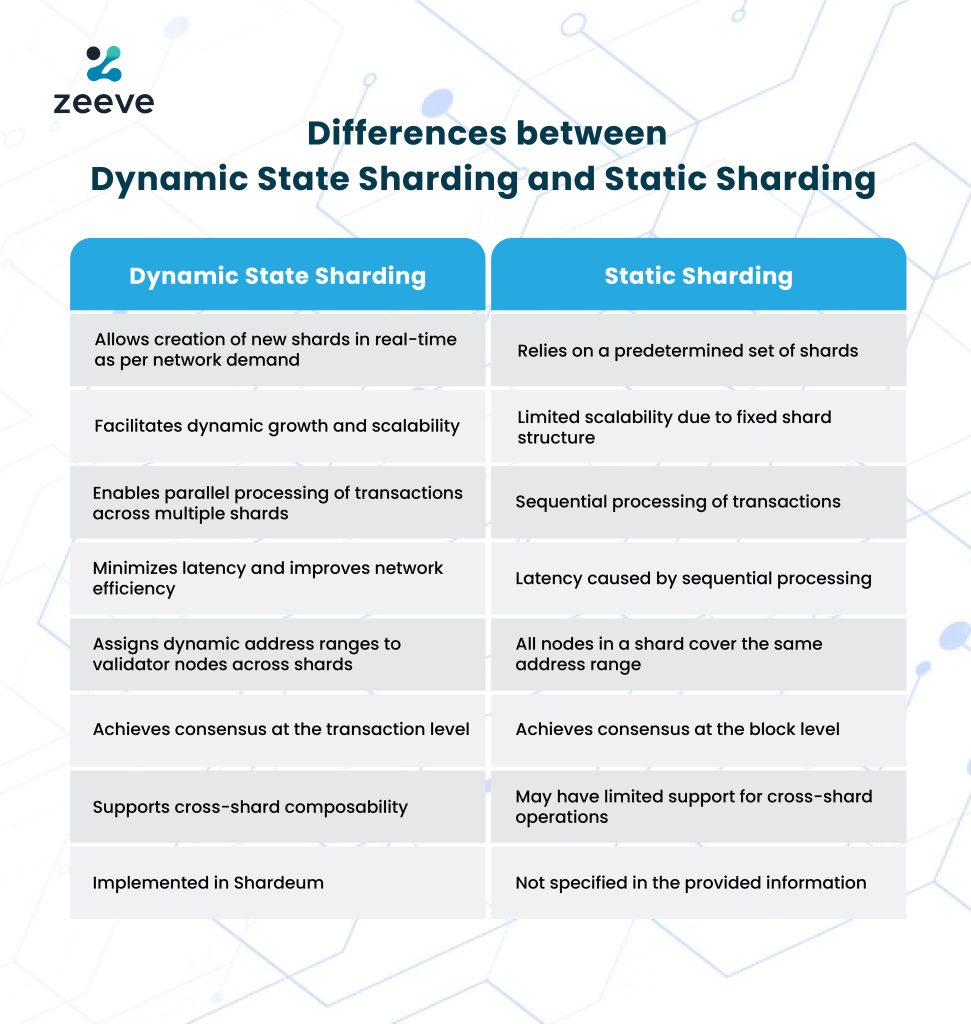
Dynamic state sharding holds immense significance in the realm of Shardeum. Its importance lies in enabling the network to sustain consistently low transaction fees for both developers and end users. It is crucial to clarify that dynamic state sharding represents the cutting-edge iteration of sharding techniques, encompassing state, transaction/network, and static state sharding.
In contrast to previous versions, this solution adeptly addresses various challenges including extended latency, vertical scalability (as opposed to linear scalability), sybil attacks, limited finality, and the absence of cross shard composability. However, it is essential to note that dynamic state sharding also stands as the most intricate approach to partitioning a network’s state.
Shardeum operates with a network that lacks a predetermined set of fixed shards or nodes. Instead, nodes within the Shardeum network possess the freedom to relocate and adapt to accommodate varying amounts of data, functioning as dynamic shards. The implementation of dynamic state sharding is seamlessly integrated with Shardeum’s auto-scaling capability. As a result, the network can autonomously regulate the quantity and dimensions of shards in response to the existing workload. This dynamic adjustment empowers the system to enhance performance and sustain exceptional scalability as it expands and progresses.
Limitations of static sharding overcome by dynamic sharding
Dynamic state sharding on Shardeum overcomes the limitations of static state sharding by allowing the network to adapt and expand based on changing demand. It addresses two critical issues: facilitating dynamic growth by creating new shards in real-time to accommodate increasing demands, and eliminating the bottleneck caused by sequential processing in static state sharding. With dynamic state sharding, transactions can be processed in parallel across multiple shards, improving network efficiency and reducing latency. By adopting dynamic state sharding, blockchain networks can achieve scalability and improved performance. On Shardeum, dynamic state sharding assigns dynamic address ranges to validator nodes across multiple shards, achieving consensus at the transaction level and supporting cross-shard composability.
Features of Shardeum that Help WIth Solving Blockchain Trilemma
Atomic Processing & Cross Shard Composability
In a sharded environment, cross-shard communication allows transactions to access and utilize data from different shards. This enables the execution of challenging transactions and smart contracts. Atomic composability ensures that transactions are executed atomically, minimizing the risk of failures or an inconsistent blockchain state. Shardeum ensures effective execution of complex transactions and smart contracts while maintaining blockchain integrity and consistency.
Linear Scalability on Shardeum
By adding nodes from its ‘standby’ validator pool during peak demand, Shardeum’s network achieves instant increases in transaction throughput. This unique feature allows the network to scale linearly, making it the first Web3 network with such capability. This scalability positively impacts various aspects of the blockchain network, including throughput, decentralization, security, and transaction fees that remain constant regardless of network demand. Shardus, Shardeum’s underlying protocol, has already demonstrated 500 TPS with 100 nodes in the past three years. Shardeum has set its sights on attaining even greater figures, targeting a potential milestone of 1 TPS (transactions per second) or higher per node. This accomplishment would represent a notable advancement for the Web3 ecosystem. In comparison, existing blockchain networks with around 2,000 active nodes can only process an average of 350 TPS, while traditional Web2 platforms like PayPal and Visa process an average of 5,000 TPS daily. Shardeum envisions mobilizing millions of nodes, enabling over 1 million TPS and empowering DApps to serve billions of users while eliminating middlemen exploiting data and privacy.
Consensus Algorithm on Shardeum
Shardeum utilizes a unique consensus algorithm called Proof-of-Quorum (PoQ) to validate and update transactions. Unlike traditional algorithms like Proof-of-Work (PoW), PoQ allows nodes to validate transactions individually upon receipt, followed by sharing the information with other nodes in a consensus group. This strategy guarantees that all nodes within the group possess knowledge of every transaction, resulting in a trustless assembly of votes or a quorum in the form of receipts. When more than 50% of the receipts are obtained, transactions are confirmed and updated on the network. Before being sent to archive nodes, individual transactions are grouped together.
Shardeum aims to enhance security through a unique combination of Proof of Quantity (PoQ) and Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms. A specified amount of coins is required to be staked, thereby reducing the risk of potential misbehavior. Additionally, the network assigns a random ‘node ID’ to validator nodes using the consensus algorithm. In addition to validator and archive nodes, Shardeum also includes standby nodes, which serve as backups and can accommodate increased demand. The network dynamically rotates validator and standby nodes using the node IDs, making it highly challenging for malicious actors to seize control of the network.
Autoscaling & Anyone Can Operate a Node
Auto-scaling is a crucial feature that allows a network to adjust its capacity according to demand. Shardeum’s protocol automatically detects the network’s current capacity and adjusts the number of active validator nodes and shard size accordingly. This ensures optimal performance and incentivizes the network to operate efficiently. Additionally, Shardeum aims to promote decentralization by making it easy for average individuals to join and operate a node with minimal resources. Validator nodes only need to maintain the current state within a shard, while historical data is stored in archive nodes. Running a node on the network is affordable and helps reinforce security while enabling horizontal scaling.
Final thoughts on the significance of Shardeum in the blockchain space
Shardeum operates on the guiding principle of being Open, Collaborative, and Community Driven (OCC). The project’s EVM-based network is developer-friendly, eliminating concerns about rising gas fees and enhancing the user experience of DApps. Instead of competing with other L1 networks, Shardeum aims to disrupt the under-utilization of blockchain technology and become a beacon of hope for existing and future Web3 platforms. By focusing on delivering a transformative impact, Shardeum recognizes the enthusiasm of today’s youth in actively working towards a more equitable world.
By combining innovative techniques such as sharding, proof-of-stake consensus, and decentralized storage, Shardeum has managed to address the challenges of scalability, security, and decentralization in a remarkable way. Its ability to process a high number of transactions per second, maintain a robust security protocol, and distribute data across a network of nodes make it a compelling option for developers and businesses alike. With Shardeum, the blockchain trilemma is no longer an insurmountable obstacle, paving the way for a more scalable, secure, and decentralized future for blockchain technology.
Get in touch with experts at Zeeve for Shardeum deployment
Choosing Zeeve for Shardeum deployment is a game-changer for developers and participants alike. The partnership between Zeeve and Shardeum aims to streamline the deployment and management of Shardeum validators, offering a simplified process and wider accessibility to the recently launched Sphinx betanet. By integrating with Zeeve, early adopters can easily join the Shardeum network as validators and earn rewards in testnet SHM. Their participation not only contributes to enhancing the blockchain’s security and decentralization but also allows them to benefit from the seamless management of validator nodes provided by Zeeve. With features such as fully automated setup and effortless node management, users can earn rewards without requiring any technical expertise. By choosing Zeeve, users unlock a world of opportunities in the Shardeum ecosystem, making their journey into blockchain deployment and management hassle-free and rewarding.
In conclusion, Zeeve stands out as the ultimate choice for Shardeum deployment. With its unparalleled reliability and robust security measures, Zeeve has emerged as the leading blockchain infrastructure management platform in the market. By offering support for all major blockchain protocols, users can effortlessly deploy nodes and networks while seamlessly launching their decentralized applications (dApps). Boasting an extensive community of over 25,000 developers, a staggering 4,000 nodes, and partnerships with more than 100 large enterprises, Zeeve continues to pave the way for a more decentralized future.