youWe-Blockchain is a technology that requires collaboration to deliver maximum value and effect to enterprise needs. Many companies today have partnered with competitors and allies in an industry to realize the benefits of a Blockchain consortium with good planning, investment, and commitment in place.
Blockchain is a technology that requires collaboration to deliver maximum value and effect to enterprise needs. Many companies today have partnered with competitors and allies in the industry to realize the benefits of a Blockchain consortium with good planning, investment, and commitment in place.
A Blockchain consortium is a trustless decentralized network. Distributed ledgers offer business-to-business workflows which are proof of the fact that Blockchain functions best when there is collaboration on set standards, infrastructure development, and transaction executions. Blockchain consortia are mediums through which mutually interested companies, regulators, and governments are collaborating to cater to their best interests in Blockchain.
This blog will give you a quick pill of knowledge about the processes involved in a consortium Blockchain network right from formation to management.
The Emergence of Blockchain Consortia
Globally, there are more than 40 Blockchain consortia belonging to different industries. Banking and Financial services have attracted significant investments.
Today we have business-focused and technology-focused consortia. The former type seeks to build and operate Blockchain based business platforms to solve a specific business problem. While the latter seeks to develop reusable blockchain platforms based on technical standards to promote cross-industry Blockchain technologies.
In case, you are wondering whether to participate in consortium blockchain or not check the pie chart below.
Why do companies join Blockchain Consortia?
Consortia exhibit a low-risk factor when it comes to efforts in staying relevant and progressive in Blockchain trends. It helps enterprises watch out for new potential opportunities in Blockchain innovations. Consortia allow companies to take advantage of Blockchain network effects. Thus it makes sense for enterprises to explore leading industry consortia.
The Formation Process
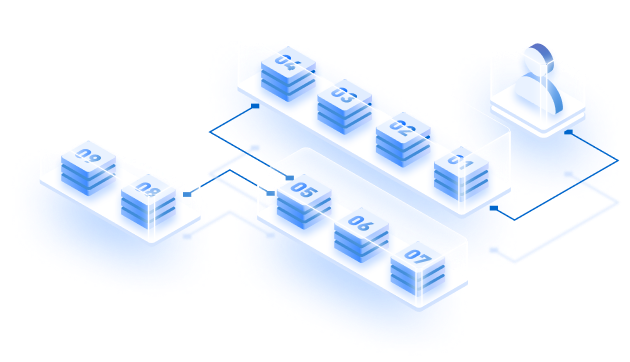
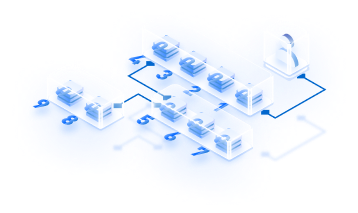
The entire process of Blockchain Consortium formation, deployment, and management is delineated below using Hyperledger Fabric on Azure as an example.
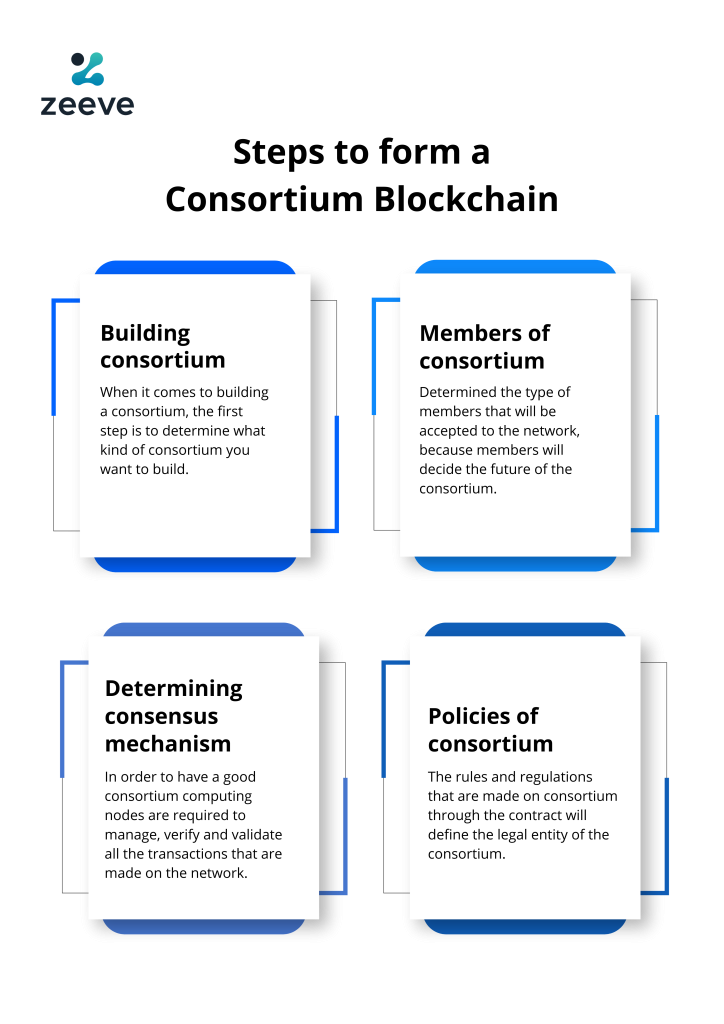
Determining the type of consortium:
The first step involves deciding what type of consortium we are looking to build after conferring with the rest of the founding members. We need to address the question- “what kind of use cases to implement?”. Are we going to build a specific use case among the founding members only? Or do we need additional members to join in?
Do we need to build a private consortium in that case? Or are we looking to build a sectoral consortium or publicly available consortium where anyone fulfilling a set of basic requirements could ask to join and build their use cases/applications with any other member of the network? In such a case, do we need to build a semi-public/permissioned consortium?
Determining the members of the consortium:
Once the founding members have decided the type of network that they want to build, the type of members that will be accepted to the network needs to be determined. The founding members need to decide if only big corporations will be included in their party.
Some other questions that need answers are, will potential new members need to be voted by the governance entity? Will there be a limit to join to a specific sector or field of activity? What is paramount in this stage is a clear consortium mission.
Determining the type/role of members:
Members may join for governance, voting power in the consortium for technical/political decisions, strategy, and roadmap. Full members may have full privileges over the network to deploy their applications, query and store data in the ledger, or participate in the consensus and validation algorithm. Partial members can deploy applications and query store any information in the ledger as read-only regulating members without validation permissions. The members may allow users to use their applications.
Policies, regulations, and constitution of the consortium: When joining the consortium all the founding and joining parties will need to accept the rules and regulations of the consortium through contract signing. This contract will define the legal entity of the consortium.
Determining the best consensus mechanism
The second layer of peer-to-peer computing nodes is required to manage, verify and validate all the transactions that are made on the network. This process of validation is called reaching consensus and it includes various algorithms such as proof-of-stake, proof-of-work, proof-of-importance, delegated proof-of-stake, PBFT, PoET, etc.
Designing the architecture
After selecting the platform, the next step is to select the internal structure of the node. You can choose from private Blockchains, public Blockchains, consortium Blockchains, and hybrid Blockchains depending on your business requirement. Before this process, you will need to get your hardware and software configurations assessed, your requirements evaluated, and suggestions on the best infrastructure for your nodes to run on.
For Hyperledger Fabric, two primary deployment types are as follows:
- Single virtual machine, developer server – This deployment type provides a development environment to build, and test solutions built on Hyperledger Fabric.
- Multiple virtual machines, scale-out deployment – This deployment type suits environments that model a consortium of different participants leveraging a shared environment.
In either model, the building blocks of the core Hyperledger Fabric are the same. The differences in the deployments lie in how these components are scaled up.
If developers prefer a low footprint server to develop applications without regard for fault tolerance, the Single virtual machine architecture is the best choice because of its lightweight nature. The multiple virtual machine architecture ensures high availability and scaling of each component at the core. Production grade deployments are usually implemented using this model.
Steps to Deploy HyperLedger Fabric on Azure
To begin, you need a platform subscription that supports deploying several virtual machines and standard storage accounts. Once you have a subscription, you need to configure the application and create a blockchain resource.
Configuring the Application
Configuring the right application is crucial before you start a project. Blockchain experts will help you choose your configuration wisely after considering elements such as Block signatures, key management, permissions, and address formats.
On Azure, this step includes configuring the multi-node Hyperledger Fabric network. There are four steps of deployment flow: Basics, Consortium Network Settings, Fabric configuration, and Optional components.
The Basics configuration option lets you specify values for standard parameters for any deployment. These include subscription, resource group, and basic virtual machine properties. The parameters used in this step are:
- Resource prefix for provisioning as part of the deployment
- The user name of the administrator for each of the virtual machines deployed for this member
- The authentication type
- The password for the administrator account for each of the virtual machines deployed
- The secure shell key used for remote login
- The subscription to which to deploy
- The resource group to which to deploy the consortium network
- The location to deploy the first member
The consortium network settings help specify inputs for the creation and participation in the existing consortium network and organization settings.
The parameters used here are:
- Network configuration for new or existing network
- HLF CA password to generate certificates by the certificate authorities
- Organization set up for the organization’s name and certificate (you can use default values also)
- VPN settings to provide a VPN tunnel gateway for accessing the VMs
Fabric-specific settings include configuring the network size and performance, specifying inputs for network availability like number orderer and peer nodes, persistence engine used by each node, and the VM size.
The parameters used are:
- Scale type for determining the deployment type of either a single virtual machine with multiple containers or multiple virtual machines in a scale-out model
- VM Disk Type determines the storage backing for each node being deployed
- Multiple Virtual Machine Deployment needs additional settings for the following parameters:
- The number of ordered nodes that organize transactions into a block
- The VM size used for orderer nodes in the network
- The number of peer nodes owned by the consortium members executing the transactions and maintaining the ledger state and copy
- Node state persistence, which determines the persistence engine used by the peer nodes
- Peer node VM size used for all network nodes
Before deployment, you need to review and accept the legal and privacy terms. Next, you develop the application and chain code for your Hyperledger consortium blockchain network.
Building the APIs
Many companies prefer building their APIs for performing audit-related functions, authenticating data through digital signatures and hashes, generating key pairs and addresses, or using Blockchain for data storage and retrieval, smart contracts, and smart-asset lifecycle management. Today, pre-built APIs can be customized to suit individual enterprise needs.
Managing Blockchain Consortium Members, the Network, and Smart Contracts
BaaS Platforms like Zeeve offers an interactive shell to members with administrator privileges to invite, add, remove, and change roles for all participants in the blockchain consortium, while user consortium members have the view and change member name privileges only.
Network Cmdlets and smart contracts help establish a connection to the blockchain endpoint’s smart contracts that are responsible for consortium management.
- An Import Consortium Management Contract cmdlet connects to the consortium management’s smart contracts using the root contract address and the Web3Client object obtained from New-Web3Connection
- The cmdlet to import the Web3 account helps create an object to hold the information for a remote node’s management account
- The cmdlet for the new web3 connection helps establish a connection to the RPC endpoint of a transaction node
Consortium member management cmdlets help manage members within the consortium.
- Get Blockchain member details or list members of the consortium
- Remove a Blockchain member
- Set blockchain member attributes, including the display name and the consortium role
Invitation management cmdlets help manage invitations within the consortium. These include:
- New Blockchain member invitations
- Retrieving or listing a consortium member’s invitation status
- Revoking a Blockchain member invitation
- Setting the Role for an existing Blockchain member invitation
Final Thoughts on Consortium Blockchain
A consortium blockchain is suitable for organizations where there is a need for both public and private blockchains. Through blockchain consortia, it is possible to leverage the potential of blockchain to increase operational efficiency and power new business models and client solutions.
Blockchain’s ability to increase operational efficiency and power new business models and client solutions is made possible through a blockchain consortium. Any organization can build and set goals using open-source platforms as per the industry.
About Zeeve
Zeeve Platform features a standardized approach to deploy reliable Blockchain nodes and networks. It means better security and compliance and cost optimization for your Blockchain. Checkout features of Zeeve No Code Blockchain Platform or sign up for a free account. More than 2000+ developers and Blockchain companies across the globe trust Zeeve for deploying and managing their Blockchain DApps, Smart Contracts and underlying infrastructure. Zeeve supports standardized deployments for multiple Blockchain Protocols. Zeeve also supports all the major cloud providers for hosting and managing your Blockchain. This includes AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Digital Ocean and IBM Cloud. Contact us today or sign up to learn how Zeeve experts can help you reap the benefits of Consortium Blockchain networks.